Dear friends of Checkmk,
the new stable release 2.0.0p9 of Checkmk is ready for download.
This maintenance release ships with 32 changes affecting all editions of Checkmk, 3 Enterprise Edition specific changes and 0 Managed Services Edition specific changes.
- Apr 23, 2020 Download the latest version of Checkmk Enterprise – Free Edition for CentOS 7 and transfer it to existing Checkmk Raw Edition Server Install the checkmk enterprise free edition email protected tmp# yum install check-mk-enterprise-1.6.0p11.demo-el7-38.x8664.rpm.
- Apr 24, 2015 Once epel has been enabled we continue to install CheckMK by placing the download package somewhere on your server. # yum install /tmp/check-mk-enterprise-1.5.0p1-el6-38.x8664.rpm. At the end of the installation we are ready to run the first site. CheckMK provides an omd command which allows the management of sites and clusters.
Changes in all Checkmk Editions:
BI: * 12661 FIX: BI aggregation datasource program: Fixed “By aggregation name” filter
Checks & agents: * 12326 SEC: Windows agent binary files are code signed * 12990 FIX: allnet_ip_sensoric_humidity: Discover On Devices With Newer Firmware * 13117 FIX: cisco_vpn_tunnel: Fix ValueError: could not convert string to float: ' * 12994 FIX: Add IPMI event “transition to OK” with OK state * 13026 FIX: agent plugin mk_db2.linux: fix timeout * 12086 FIX: alcatel_power_aos7: throws exception “KeyError()” on empty power_type_entry * 13031 FIX: arista_bgp: handle empty addresses * 13030 FIX: check_mk_agent terminates ntpd via timedatectl * 11814 FIX: smart check: Evaluate command timeouts as counter * 13028 FIX: solaris agent: ps: don’t cut user names after 8 chars * 11812 FIX: esx multipath: Skip devices without LUN ID
Core & setup: * 13074 API: modification of acknowledgement endpoint to allow management in distributed setup * 12955 FIX: host collection response in REST API NOTE: Please refer to the migration notes! * 12956 FIX: REST API exception handling * 13033 FIX: REST API: respect disabled WATO
HW/SW inventory: * 12989 FIX: mem_used: “KeyError: ‘SwapTotal'”
Notifications: * 13027 FIX: Bulk notification without WATO plugin crash * 12849 FIX: Fix service label notitification condition
Setup: * 13066 SEC: Fix path traversal vulnerability * 12846 FIX: Fix inheritance of folder contact groups to services of hosts NOTE: Please refer to the migration notes! * 12848 FIX: Fix remote host renaming timeouts in distributed setups * 12851 FIX: Folder/Host permissions: Users could add groups but not remove them afterwards * 12687 FIX: activation_cleanup: fix growing tmp directory due to inactive cleanup job
User interface: * 12845 FIX: Cleanup redundant custom sidebar snapin permission * 12993 FIX: Filter Multiple WATO folder can now be saved * 12663 FIX: Fixed steadily rising CPU load due to misconfigured dashboard dashlets * 12995 FIX: Graph don’t confuse metrics names that are like numbers for values * 12847 FIX: LDAP: Fix handling of groups containing “#” in Active Directory * 13097 FIX: Make host search more flexible on parent search * 12805 FIX: Overlapping label inputs (label conditions) * 12996 FIX: Performance graphs always use default color styles
Changes in the Checkmk Enterprise Edition:
Core & setup: * 12304 FIX: Fix case where passive checks would remain “passive” until a core restart
Livestatus: * 12988 FIX: Logging Level For Liveproxy Daemon
User interface: * 13136 FIX: SLA View: Displaced timelines
Changes in the Checkmk Managed Services Edition:
Welcome to the Checkmk Customer Portal. Please login with your download credentials to see information about your subscription and download the Checkmk Enterprise.
You can download Checkmk from our download page: * checkmk.com/download.php
Please mail bug reports and qualified feedback to feedback@checkmk.com. We greatly thank you for using Checkmk and wish you a successful monitoring,
Your Checkmk Team

Do your want a Linux-based Website or IT infrastructure monitoring tool? Try out Checkmk on Ubuntu Linux, which is an open-source but enterprise-level Linux platform to monitor the health and activity of various servers and machines available in the network. Its monitoring kernel is based on Nagios.
When you have multiple machines in a network or cluster of servers then knowing their condition is extremely important. In such situations, we can use Checkmk like open-source Linux software for network monitoring, which meant to handle thousands of computers and devices. Pretty much everything from the router to the ink level in the printer to running processes on Windows computers can be monitored. And sensors, services, databases, websites, cameras, and so on. Would you like to be get alerted on hacker attacks? Provision for that is also available on Check_mk.
Well, although CheckMk is a platform that can support the monitoring of hundreds of hosts that doesn’t mean it only meant to use by big enterprises. Even a startup with few couples of hosts can use it efficiently without paying any extra cost. Furthermore, even for a home user who has a couple of devices at home, Checkmk is still worth a look. For example, whether you want to monitor your home media center, web server or want to know your kid’s or parents’ laptop is up to date? Is your website up and running? How about storage space? All such things can be handled by CheckMk.
It is available in three editions Opensource, Free, standard, and managed Services. The open-source Checkmk Raw edition is available to use without any limitation and can monitor more than 1,000 hosts. However, performance will be slightly behind the Free and other Enterprise editions of CheckMk because of the optimization. You can check out the feature difference between the editions on its official website. Here we will use the open-source version which is more than enough after all we are not paying anything for it.
Well, Checkmk can collect data from systems and monitor them and for that, an agent must be installed on Windows and Linux servers. Here we will let you know the steps to install Checkmk on Ubuntu 20.04/18.04 server and then how to use the same to monitor various Linux and Windows machines available in your network.
Prerequisites
- An Ubuntu-based server with
rootaccess. - All the devices you want to monitor should on a network and accessible through the CheckMk installed Server.
Contents
- Install Checkmk On Ubuntu 20.04 to monitor Linux and Windows machines
Install Checkmk On Ubuntu 20.04 to monitor Linux and Windows machines
Note: Log in as root to run the below commands…
1. Download Checkmk Raw edition
Go to the official website of Checkmk and select the stable version than the Linux package you want to download. As here we are using the Ubuntu server, we will go for Ubuntu one available for 20.04 LTS; in a similar way, users on some old version of Ubuntu such as 19.04, 18,04, 16,04.. can download the available file corresponding to them.
If you want to install it on a remote or CLI server, then connect it using SSH and then with the help of wget command download it. For example, while writing the tutorial, the latest version of Checkmk was 1.6.0p20, thus the command will be like this:
In the same way, you can also download installation RPM packages of this platform for RHEL or CentOS servers.
2. Install Check_mk on Ubuntu/Debian or RHEL/CentOS
The installation of the tool is pretty simple and straightforward. As we already have its Debian packages, thus let’s run the command to install the same.
Ubuntu or Debian
sudo apt install ./filename
Check Mk Enterprise Edition Download
For RHEL or CentOS
After downloading the file for RHEL or CentOS
yum install filename
Example:
To check the installed version, simply run:
Note: Open Monitoring Distribution (OMD) is also an open-source project developed by Mathias Kettner to manage monitoring solutions made up of various components. In short, we can use this command tool to manage Checkmk services.
3. Creating CheckMk monitoring instance or site
To use Checkmk we have to create an instance that also known as a site. It works on the instance model so that if a server has multiple copies of Check_mk then creating an instance will isolate them from each other, hence, there would not be any kind of hindrance. However, creating a single instance will be enough. Here is the command to do that.
omd create instance-name
Replace the instance-name with whatever you want to give it. For example, here we are using h2smonit, then the command will be:
You will get output something like shown in the below screenshot. Along with details such as user name and password to login to the web application interface of Checkmk.
4. Start Checkmk Instance on Ubuntu 20.04
The instance has been created and we already have the admin credential to log in to its web interface from where we can monitor our network devices and systems. However, before that, we have to start the services of the created instance.
For that use the command- omd start instance-name, here we have used h2smonit, thus the command will be:
5. Access Check_mk web interface
Finally, our instance is up and running, now it’s time to access the web interface of this IT infrastructure monitoring solution. Open a browser on your local machine and enter the IP-address or domain name of the Ubuntu server where you have installed Checkmk along with the instance name. example- http://ipaddress/instance-name
Here our instance name is h2smonit and IP-address is 192.168.0.110, hence the URL will be – http://192.168.0.110/h2smonit/
Once you logged-in, if you want then change the Admin user password that was generated by the Checkmk’s OMD command, so that you can easily remember it.
For that, go to WATO– Configuration, select Users, click on the Pencil icon given in front of your Admin user.
Enter the Password you want to use and then click on the Save button. This will automatically log you out immediately. Now, log in again with the new password you have created.
One thing that needs to be noted, every time we make some change in the configuration of Checkmk, a yellow color Change button will get highlighted. And to implement the changes properly, click on it, select the Changes you have made, and hit the Activate it.
6. Install Checkmk agent to Monitor Linux or Windows hosts
As you see no activity would be there on Checkmk because, yet we have not told our monitoring server which machines need to be monitored.
So, whatever machine you want to be get checked by this Linux monitoring tool, we have to first install Checkmk agent on that including the Server where you have installed the Checkmk itself. To make all this easy, go to the Monitor Agent option available in the WATO configuration menu area and download the files as per the system you want. For example, Deb file for Debian and Ubuntu-based systems, RPM for RHEL/CentOS, MSI for Windows, and so on.
For example, Right-click on the file, copy the link of the file as per your Linux OS, and use the wget command to download it:
#On Ubuntu or Debian Linux
Install Xinetd- Xinetd (Extended Internet Service Daemon) is an open-source super-server daemon that manages Internet-based connectivity.
Download agent file:
To install-
Check Mk Enterprise Edition Download Pc
sudo apt install ./downloaded-file-name
example– sudo apt install ./check-mk-agent_1.6.0p20-1_all.deb
#For RHEL or CentOS Linux
As we have done for Ubuntu or Debian based system above, we will download the RPM package of Check_Mk Agent and then we will install the same.
Download file
Right-click on the RPM package and copy its link:
wget file-link
Installation
To check the installed Agent version, we can use :
#For Windows
To monitor Windows OS based system, we just need to download the MSI package of the Check_mk agent and the installation will be like any other Windows software.
On Windows, you would also need to allow the Check_mk Agent application in the firewall. For that open firewall, select Allow an app through the firewall option.
Click on change settings and then Allow another app.
After that browser the check_mk_agent.exe
7. Restricting Host to Server IP-address only
Our Check_mk server will read the host’s vital health information with the help of check_mk_agent and using telnet to port 6556. However, for security reasons, it will be a good idea, if we restrict the host installed Agent to send information only to Check_mk Server Ipaddress.
On Linux systems edit xinetd file:
And uncomment only_from and type the check_mk server IP address in front of it. And save the file by Ctrl+X, type Y and then hit the Enter Key.
On Windows, we can restrict it using the firewall easily…
8. Add host to Check_Mk
On the Web interface of this monitoring tool, select the Hosts from the WATO configuration and then select the New Host option.
Check Mk Enterprise Edition Download Pc
Enter the hostname of the host you want to add and monitor on Check_mk.
If you don’t know the hostname then you can find it by typing the command- hostname on the machine, you want to monitor.
After that save and test it.
Once you have added hosts successfully, activate them. For that you will see again a yellow color Change button on the Top Menu, select that, and hit the Activate affected button.
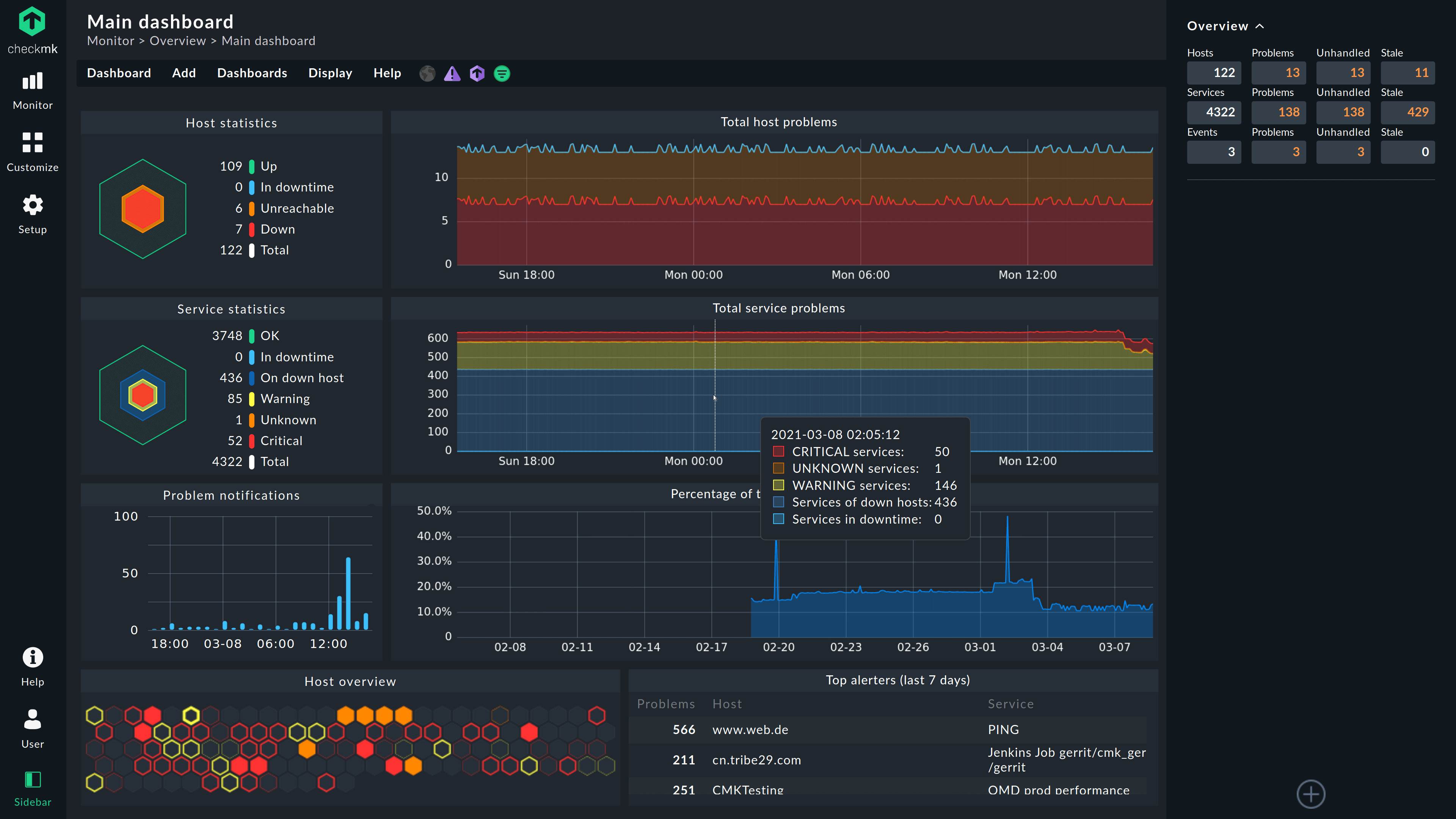
9. Main Overview- Report
Now, on the main Dashboard screen, you will see two globe icons along with hosts information such as how many hosts are up and down, unreachable, Downtime, errors, and more. To know further we can also use the All hosts option given under the View menu and from there select the hosts individually to see further details.
Check_MK Tutorial verdict…
Checkmk Enterprise Edition Download
This tutorial is just an introduction and installation of Checkmk Linux monitoring server on Ubuntu, however, there are lots of features that one can know in detail from the official documentation.